The bane of the internet, cybercrime refers to any and all illegal activities carried out using technology. Cybercriminals — who range from rogue individuals to organized crime groups to state-sponsored factions — use techniques like phishing, social engineering, and all kinds of malware to pursue their nefarious plans. Find out how cybercrime works and how to protect yourself here.
What is cybercrime?
When you hear the word “cybercriminal” or “hacker,” what image comes to mind? Is it a sketchy guy, perhaps wearing a dark hoodie, camped out in a dank basement somewhere, typing away furiously? While that image is in the public consciousness thanks to movies and TV, the real picture of a cybercriminal is much different
1.Phishing scams Phishing is a practice of a cybercriminal or hacker attempting to obtain sensitive or personal information from a computer user.

2. Identity Theft scams Cybercrooks who may have gained access to your credit card or banking account information may use that information to make purchases in your name.

3. Online Harassment Harassment online is usually related to your social lifestyle and if you choose to use a popular social network such as Facebook or Twitter.
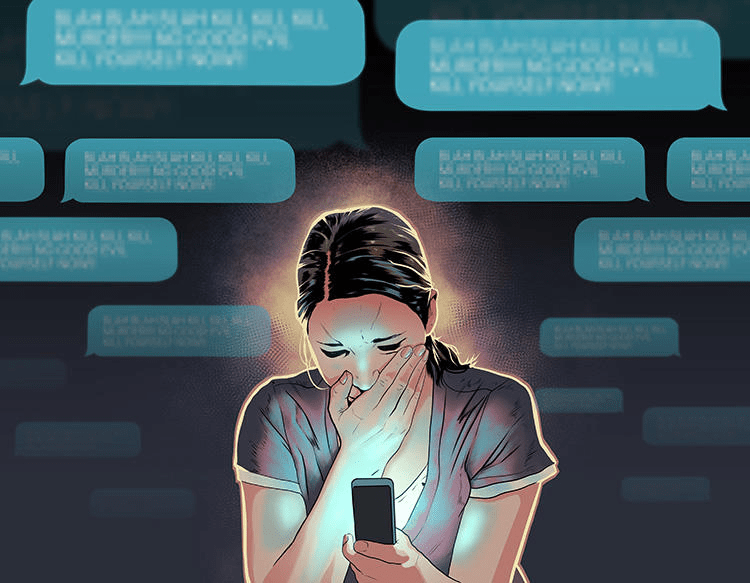
4. Cyberstalking Cyberstalkers will go to great lengths to try to monitor a victims online activity. This may include infecting a person’s computer with malware that is able to log computer activity.

5. Invasion of privacy The invasion of privacy is basically the act of someone attempting to intrude on a person’s personal life.

10 Ways to Prevent Cyber Attacks
Even if you don’t currently have the resources to bring in an outside expert to test your computer systems and make security recommendations, there are simple, economical steps you can take to reduce your risk of falling victim to a costly cyber attack:
- Train employees in cyber security principles.
- Install, use and regularly update antivirus and antispyware software on every computer used in your business.
- Use a firewall for your Internet connection.
- Download and install software updates for your operating systems and applications as they become available.
- Make backup copies of important business data and information.
- Control physical access to your computers and network components.
- Secure your Wi-Fi networks. If you have a Wi-Fi network for your workplace make sure it is secure and hidden.
- Require individual user accounts for each employee.
- Limit employee access to data and information and limit authority to install software.
- Regularly change passwords.
-POSTED BY: JASFER P. RULE